|
26 Feb 2016 |

|
ESA's exploration strategy considers the Moon as the next destination for humans venturing beyond low Earth-orbit and an integral part of the roadmap towards human missions to Mars.
The Moon 2020-2030 Symposium aimed at consolidating an international vision for lunar exploration by 2030, and discussing approaches and innovative ideas for realising this vision.
During the Symposium, space agency, academic and industrial players provided their view on how to better engage in a new era of coordinated human and robotic exploration in the interest of science and human expansion.
|
 |
01 Dec 2015 |

|
ESA honours the hundredth anniversary of the Theory of Relativity with a seminar on 26 November 2015 at ESA-ESTEC.
|
 |
26 Aug 2015 |

|
This ESA "call for ideas" represents a unique opportunity for the private sector to shape and engage as a strategic partner in the future global space exploration undertaking.
ESA wants to assess the interest of the private sector in implementing the Agency's space exploration strategy.
To date space exploration is an institutional domain led by space agencies. However, an increasing number of initiatives coming from the private sector have recently emerged that could lead to a paradigm shift in space exploration strategies.
|
 |
21 Aug 2015 |

|
Samantha Cristoforetti will be the seventh Italian astronaut to fly in space and her mission is the second long-duration mission for Italy's ASI space agency, following Luca Parmitano's Volare mission in 2013. The logo reflects Italy's involvement using the three colours of the national flag.
The Futura mission will blast off on 23 November and Samantha will follow ESA astronaut Alexander Gerst on the Space Station.
Samantha was a fighter pilot in the Italian air force before joining ESA's astronaut corps in 2009. She will be the third astronaut of ESA's new recruits to fly in space. She is fluent in many languages and her trip to the Station will be the 42nd expedition.
During the six months she stays on the space laboratory she will run new international experiments and continue the research of her astronaut colleagues.
|
 |
13 Jul 2015 |

|
ESA Astronaut Alexander Gerst left Earth from Baikonur cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, on 28 May 2014. He flew on a Soyuz spacecraft to the International Space Station with Russian cosmonaut Maxim Viktorovich Surayev and NASA astronaut Gregory Reid Wiseman.
|
 |
02 Jul 2014 |

|
the European Space Operations Centre and its network of ground stations and services Since its creation in 1967, the European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) in Darmstadt (D) has planned missions, operated more than 60 satellites and ensured that spacecraft meet their mission objectives. The mandate of ESOC is to conduct mission operations for ESA satellites and to establish, operate and maintain the necessary ground segment infrastructure. The infrastructure consists of laboratories, environmental test facilities, ground stations, operational control centres, communication networks, information systems, information technology infrastructure as well as buildings and associated facilities. |
 |
22 Apr 2014 |

|
ESA ISS science explained by the principal investigators.
|
 |
12 Dec 2013 |

|
New Materials & Energy is a project co-funded by the 7th Framework Programme of the European Commission, coordinated by the European Space Agency. |
 |
20 Nov 2013 |

|
ESA astronaut Luca Parmitano is set to fly to the International Space Station in May 2013. He will spend six months on the International Space Station on Expedition 36/37 under an agreement with Italy's ASI space agency and NASA. |
 |
17 Oct 2013 |

|
ATV-5 has been named after Belgian physicist Georges Lemaître, father of the Big Bang theory. Automated Transfer Vehicles are multi-function unmanned ferries sent into orbit by the European Ariane 5 launcher. Each spacecraft can deliver up to 7 tonnes of cargo to the International Space Station including supplies and equipment, water, air, nitrogen, oxygen and fuel. Once attached, ATV refuels the Space Station and can also reboost it: ATV's propulsion system is used to raise the Station to a higher orbit, counteracting the atmospheric drag that slowly causes the Space Station to lose attitude. ATV can even boost the Station to avoid collisions with space debris and provide attitude control. |
 |
12 Sep 2013 |

|
This latest ATV - named after German-born physicist Albert Einstein - was lowered by an overhead crane onto its Ariane 5 inside the 90-meter-tall Final Assembly Building in French Guiana. The payload fairing which will complete the launcher build up will be mounted closer to the launch date, allowing for loading of late cargo for the ATV's International Space Station servicing mission. This second Ariane 5 flight of 2013 is scheduled for a June 5 liftoff. |
 |
11 Jul 2013 |

|
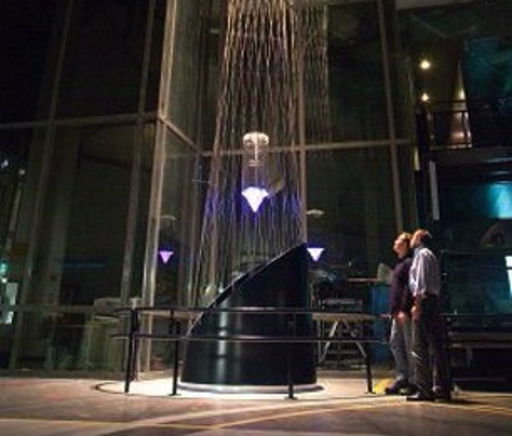
The Erasmus drop tower demonstrator is intended to promote the use of the full-sized drop tower facility at the ZARM scientific institute in Bremen, Germany. An external ESA facility since September 2003, the 146-metre ZARM drop tower provides 4.74 seconds of weightlessness %u2013 a figure which will be doubled from the beginning of next month using a catapult system at the base of the shaft. The facility is not purely an exhibit, scientists and students can also come here to ESTEC and gain first-hand experience of carrying out microgravity experiments. The drop tower demonstrator completes the picture of microgravity possibilities on display in the Erasmus Centre. As a functional model it will help to familiarise potential users with Europe's drop tower facilities. They can use the demonstrator to work on their ideas and prepare an experiment for the ZARM drop tower. |
 |
12 Feb 2013 |

|
Mission X: Train Like an Astronaut is an international educational challenge focusing on fitness and nutrition as we encourage students to "train like an astronaut." Mission X is focused on fitness and nutrition because we know that a healthy body is necessary to be a 'Fit Explorer!' The World Health Organization has designated childhood obesity as one of the most serious public health challenges of the 21st century - and diet, physical activity, and health are the best answers to this largely preventable problem. Astronauts know the vital importance of physical training for mission success, and we are excited for kids all over the world to learn from them - for life success. Teams of elementary students will learn principles of healthy eating and exercise, compete for points by finishing training modules, and get excited about the world's future in space and the educational possibilities for their own future. Students will practice scientific reasoning and teamwork while participating in hands-on training missions targeting strength, endurance, coordination, balance, spatial awareness, and more. Train Like an Astronaut mission activities include: Base Station Walkback; Crew Strength Training; Do a Spacewalk; Mission: CONTROL!; Jump for the Moon; Explore and Discover; Agility Astro-Course; Speed of Light; Building an Astronaut Core; Crew Assembly; Let's Climb a Martian Mountain; Planet you GO, Gravity you Find; Get on Your Space Cycle; and Space Roll and Roll. Educational science modules include: Living Bones, Strong Bones; Hydration Station; Energy of an Astronaut; and Reduced Gravity, Low Fat. |
 |
04 Feb 2013 |

|
SPHERES (Synchronized Position Hold Engage and Reorient Experimental Satellites) are free floating satellites designed by MIT on the ISS which, via the setting of a game, can be commanded by teams of secondary school students. The teams shall compete against each other in multiple simulation phases on ground and the most successful teams shall have the opportunity to see their code in action on the ISS, live! Here you will find videos and webcasts relevant to ZeroRoobotics.
|
 |
05 Nov 2012 |

|
ESA astronaut Andre Kuipers and crewmates Oleg Kononeko and Don Pettit docked on 23 Dec 2011 with the International Space Station in their Soyuz TMA-03M spacecraft. They will work aboard the Station now for five months and return to Earth in May.
|
 |
28 Jun 2012 |

|
On June 11, NASA sent the 16th aquanaut crew to live for two weeks in Aquarius, the world's only undersea laboratory. NASA leases the laboratory each year from the National Oceanic & Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) to conduct research and simulate mission activities in the water's low gravity. NEEMO missions are performed at Aquarius because the isolation, constrained habitat and crew quarters, harsh environment, and reduced gravity challenge aquanauts to perform mission operations despite extremely formidable conditions. Much like space, the undersea world is a hostile, alien place for humans to live. NEEMO crew members experience some of the same challenges there that they would on a distant asteroid, planet or moon. The NEEMO 16 objectives focus on asteroid mission scenarios, but the operational and technical concepts that the team is investigating are common to any long-duration human exploration mission:
Testing these mission concepts in the weightless underwater environment helps NASA understand the challenges of sending humans to explore an asteroid. Long-duration NEEMO missions provide astronauts with a realistic approximation of situations they will likely encounter on missions in deep space and provide an understanding of how to carry out daily operations in a simulated planetary environment. |
 |
08 Jun 2012 |

|
ISS SYMPOSIUM 2012 More than ten years ago, the first module of the International Space Station (ISS) began offering scientists a unique research laboratory in space. With the assembly of the Station now being complete and all ISS partner laboratories in operation, a solid and steady foundation has been laid for a wide range of research. ESA organised a high level, global ISS Symposium in Berlin from 2nd to 4th May 2012 to review and discuss the key accomplishments in research made to date, looking at case-studies in fundamental and applied research and the spin-offs for the benefit of humankind, as well as to discuss the future path and priorities for research on ISS until at least 2020. The Symposium brought together representatives from the five ISS partner agencies, other space-faring nations, the international science community, space experts, astronauts, engineers and representatives from industry, academia and media. |
 |
29 Mar 2012 |

|
ESA's third Automated Transfer Vehicle, scheduled for launch on an Ariane 5 from Europe's Spaceport in French Guiana on 23 March, is planned to dock with the International Space Station five days later. ATV-3 will automatically dock with the Station's Russian Zvezda module during the night of 28%u201329 March. The precise time will be known after launch, which is set for 04:31 GMT (05:31 CET) on Friday, 23 March. The flight of ATV-3 is part of the internationally coordinated servicing effort to support the International Space Station. |
 |
04 Oct 2011 |

|
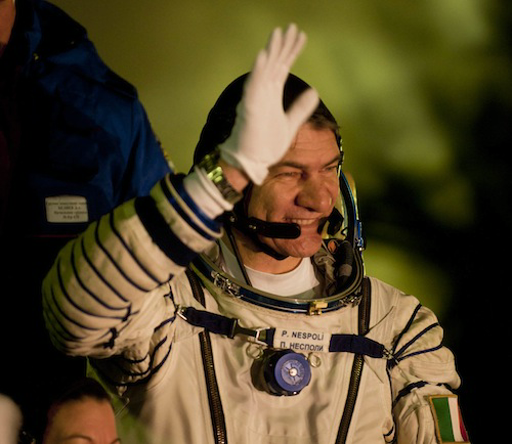
During his MagISStra mission, Paolo Nespoli will live and work on the International Space Station (ISS) with Kondratyev and Coleman as members of Expeditions 26 and 27. The Latin-flavoured name combines the word magistra, the female teacher, with the acronym of the International Space Station, continuing ESA's tradition of having ISS within the mission name. MagISStra also echoes the humanistic value of the mission, because it reflects the special link with education. It is one of the three dimensions of the flight, together with science and technology. The mission logo features a human being, who can be seen as the Paolo himself, projected from the ISS. The value of the mission to Earth is symbolised by three icons between the arms: the plant denoting scientific research, the gears for technology, and the book as knowledge. The six stars represent the six crewmembers living on the Station during the mission and the six months that Paolo will stay in space, as well as the idea of Europe. |
 |
04 Oct 2011 |

|
Roberto's mission is named DAMA in reference to the search for the mysterious dark matter that will be conducted by the 6.9-tonne fundamental physics payload, the AMS-02 Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer, probably the most ambitious science payload ever launched to the Station. AMS-02 will help scientists to understand better the fundamental issues on the origin and structure of the Universe by observing antimatter and "dark" matter. It was launched on Space Shuttle mission STS-134. Crew members are Commander Mark Kelly, Pilot Gregory H. Johnson and Mission Specialists Michael Fincke, Greg Chamitoff, Andrew Feustel and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori. |
 |
03 Mar 2011 |

|
ATV Johannes Kepler (ATV-2) is the first operational ATV, following the highly successful ATV Jules Verne qualification flight in 2008. With a total mass of over 20 tonnes, it is the heaviest payload ever launched by Europe. ATV is a highly sophisticated spacecraft, combining an autonomous free-flying platform, a manoeuvrable space vehicle and %u2013 when docked %u2013 a space station module. To achieve an automated docking under the very tight safety constraints imposed by human spaceflight rules, ATV carries high-precision navigation systems, highly redundant flight software and a fully autonomous collision-avoidance system with its own independent power supplies, control and thrusters. About 10 m high with a diameter of 4.5 m, ATV includes a 45-cubic m pressurised module and a Russian docking system, similar to those used on the Soyuz manned ferries and the Progress resupply ships. With its solar wings deployed, ATV spans 22 m. Almost three times larger than Russia's Progress, it can also deliver about three times the cargo load. ESA's latest Automated Transfer Vehicle is ready for launch to the International Space Station on Tuesday, 15 February at 22:08 GMT from Europe's Spaceport in Kourou, French Guiana. The unmanned spaceship will deliver essential supplies and reboost the Station during its mission lasting three and half months. |
 |
20 Jan 2011 |

|
The SEEDS post graduate MSc course is a 15-month programme organised by three leading European aerospace universities: the Politecnico of Turin, in Italy, the University of Bremen, in Germany, and the Grande Ecole Aérospatiale Supaero in Toulouse, France. All three universities are based in cities that host space industries and research centres, and have a long-standing tradition of cooperation in space. This guarantees the support and contribution of high-level experts and strong links with space industry and agencies. As part of the programme, students attend preparatory courses on "Understanding Space: Introduction to Space Basic Concepts" and on "Learning about Space Systems: fundamentals of Space Engineering", and perform an intensive activity of Preliminary Design while engaged in a 6-month project conducted in Toulouse, Bremen and Turin. The SEEDS course differs from other MSc and post-MSc space programmes in that it focuses on the design habitable systems for space exploration. It aims to prepare the future workforce needed by the European space industry with a special focus on system engineering of space exploration programmes. During the past few years, the SEEDS course has been endorsed by ESA, the Italian space agency (ASI), the French space agency (CNES), the German Aerospace Centre (DLR), Thales Alenia Space, Astrium, OHB Systems and other companies from the European space industry. Thales Alenia Space plays a leading role in defining the academic curriculum of the course. Today, ESA's Directorate of Human Spaceflight is actively defining its role in the International Space Exploration Initiative. This is why having system engineers for human space exploration trained through the SEEDS programme is an excellent investment for the future of Europe. |
 |
02 Dec 2010 |

|
ASTRO BITES: ISS for Future Exploration.
The six new European astronauts are getting ready to use the International Space Station (ISS) as a testbed for future space exploration. Having in mind the challenges that long-duration flights will pose, these videos explain some of the threats they will face in space and the solutions they may need. After a decade in orbit, the life extension of the ISS offers an ideal opportunity to test the new capabilities and technologies needed for venturing further into the Solar System. The European Space Agency is gathering fresh ideas for the final testing and initial use of experiments, spacecraft systems or robotic assistance on the Station. |
 |
10 Aug 2010 |

|
Videos and highlights on ESA Parabolic Flight Campaigns.
|
 |
24 Jun 2010 |

|
The IMPRESS Integrated Project is a large pan-European flagship project in the field of applied material science. IMPRESS is an acronym for "Intermetallic Materials Processing in Relation to Earth and Space Solidification". The project is managed by the European Space Agency and is co-funded by the European Commission in the 6th Framework Programme. IMPRESS comprises a large multi-disciplinary consortium of 42 research groups and companies, with a total 5-year budget of 41 million Euros. By combining the expertise of 150+ leading scientists from 15 countries, IMPRESS now has the potential to make Europe a world-leader in the strategically-important area of intermetallic materials and application. Within the framework of this project a series of on-line Video-on-Demand lectures by European material science experts is being created. |
 |
05 Feb 2010 |

|
Node 3 and Cupola were launched on the Space Shuttle Endeavour, STS-130. Shuttle flight STS-130 was launched on Monday 8 February at 10:14 CET from NASA's Kennedy Space Centre (KSC). It delivered Node 3 (named "Tranquility" by NASA), one of the three ISS interconnecting modules that houses the life support equipment necessary for a permanent crew of six. This mission also carried the European-built Cupola observation module, a seven window dome-shaped structure from where the Space Station's robotic arm can be be operated and the crew has a panoramic view of space. |
 |
13 Oct 2009 |

|
OasISS mission, ESA's second long-duration mission to the International Space Station (ISS). This flight saw Frank De Winne, from Belgium, become the first European to take command of the largest human outpost ever assembled in space. When De Winne, Romanenko and Thirsk arrived on the ISS in May 2009, they joined the three resident astronauts to form the first permanent crew of six, allowing more scientific experiments to be conducted onboard. |
 |
24 Sep 2009 |

|
The Alissé mission is ESA astronaut Christer Fuglesang's second spaceflight. The mission gets underway with the launch of Space Shuttle Discovery from NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The launch of Discovery on Shuttle flight STS-128 is scheduled for 25 August 2009. A principal focus of Fuglesang's mission is his spacewalk activities as a Mission Specialist for STS-128. Fuglesang also undertakes experiment, educational and public relations activities as part of the Alisse' Mission. |
 |
22 Sep 2009 |

|